Introduction to metal and non-metal oxides
Key points
- Metals and non-metals can react with oxygen to make compounds called oxides.
- Metal oxides act as bases. This means they can neutralise an acid.
- Non-metal oxides usually dissolve in water to make acidic solutions.
A video about oxidation reactions
A video that shows what happens when metals and non-metals are combined with oxygen
When substances combine with oxygen the process is called oxidation and the compounds made are called oxides.
The sparks in fireworks are made by burning different metals. The burning metals are reacting with oxygen in the air and producing metal oxides.
Sparklers contain small pieces of iron. When you burn the iron it reacts with oxygen to make iron oxide, creating the sparks we see.
When a sparkler has finished burning, you’ll notice that the iron pieces on the rod have changed colour.
This is because when the iron is heated, oxidation takes place. The iron oxide is no longer a pure metal, it is a dull, dark-coloured, metal compound.
When you burn magnesium in the air in the same way that the iron did, the magnesium reacts with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide. Magnesium oxide is a dull white powder.
When we add water the magnesium oxide dissolves to form a solution that turns red litmus paper blue, telling us it is alkaline also called a base. So this shows us that metal oxides are bases, when added to water.
Some non-metals can also react with oxygen in an oxidation reaction. When burnt in oxygen, the carbon in this charcoal reacts to form carbon dioxide.
When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it forms a solution, which turns blue litmus paper red, telling us that non-metal oxides are acidic.
List some of the typical properties of metals.
Metals can be:
- good conductors of electricity and heat
- hard
- malleableCapable of being hammered or pressed into a new shape without breaking.
- shiny
- high in density
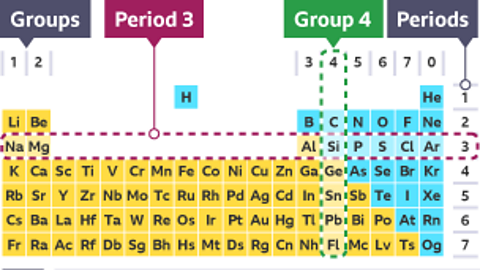
Metals in the periodic table
Metals are found on the left and in the middle of the periodic tableA table which lists all of the chemical elements.
A line of steps underneath boron (B) can be drawn to divide the table into metals and non-metals.
Oxides
compoundA pure substance made from two or more elements which are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. are substances made of two or more types of atomThe smallest particle of an element. We often think of atoms as tiny spheres, but in fact they are made from smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. chemically bonded together. All oxideA compound which contains an element bonded to oxygen. are compounds, and contain a single element bonded with oxygen.
For example:
- magnesium oxide has the chemical formula MgO, and contains only magnesium (Mg) and oxygen (O)
- sodium oxide has the formula Na‚ÇÇO and contains only sodium (Na) and oxygen
- aluminium oxide has the formula Al‚ÇÇO‚ÇÉ and contains only aluminium (Al) and oxygen

Did you know?
Some chemical formulas contain little numbers called ‘subscripts’. They represent the number of atoms of each element in the formula. For example, CO₂ contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.

When non-metalA substance that has the typical properties of a non-metal. Non-metal elements are on the right hand side of the periodic table. oxides are named they include a prefix at the beginning of the word ‘oxide’. These prefixes show how many oxygen atoms are in the oxide.
For example:
- carbon **mon**oxide has the formula CO, it has one oxygen atom
- carbon **di**oxide has the formula CO‚ÇÇ, it has two oxygen atoms
- sulfur **tri**oxide has the formula SO‚ÇÉ, it has three oxygen atoms
The prefixes match up to the number of oxygen atoms.
Silicon has the symbol Si. What is the formula of silicon dioxide?
≥ßæ±∞ø‚ÇÇ.
The word dioxide tells us that for each silicon atom (Si) there must be two oxygen atoms.
Forming oxides
When an element reacts with oxygen a chemical bond is formed. The compound formed is called an oxide. This can be written as a chemical equationA way of describing chemical reactions in words or symbols..
Chemical equations can be written as word equations or symbol equations. For example, the word equations:
calcium + oxygen ‚Üí calcium oxide
carbon + oxygen ‚Üí carbon dioxide
Or the symbol equations:
Ca + O‚ÇÇ ‚Üí CaO
C + O‚ÇÇ ‚Üí CO‚ÇÇ
Some elements will react with oxygen in the air at room temperature. For example, sodium reacts with the oxygen in air to produce a white coating of sodium oxide. When the sodium is cut, the fresh shiny sodium is visible.

Lots of metalA substance which has the typical properties of a metal. Metals are found to the left and in the middle of the periodic table. are less reactiveThe tendency of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction. than sodium. They require heating in a Bunsen burner A piece of apparatus that uses gas to apply heat in some experiments. It is named after the chemist, Robert Bunsen. to make the reaction occur.
For example, when a strip of magnesium is heated in a Bunsen burner a bright white flame is seen. The magnesium reacts with oxygen in the air. The shiny grey magnesium strip changes to a white powder called magnesium oxide.
Learn more about making a reactivity series in this guide.

When magnesium is heated with a Bunsen burner it forms magnesium oxide. Where do the oxygen atoms come from?
The air.
The air contains approximately 21% oxygen.
Properties of metal and non-metal oxides
Metal oxides
Metal oxides are solids. One of the properties of metal oxides is that they act as baseA substance which neutralises an acid. . This means that they are able to neutraliseWhen an acid reacts with a base and this results in the pH of a solution moving towards 7. acidA substance which produces hydrogen ions in solution. Acids have pH values lower than 7. , producing a salt plus water.
Some metal oxides react with water to make an alkali, a solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water. which has a pH scaleA scale which gives a value for how acidic or alkaline a substance is. higher than 7. Alkalis also neutralise acids to produce a salt plus water.
For example, sodium is burned to make sodium oxide. Sodium oxide is a base because it can neutralise an acid. Sodium oxide can be reacted with water to produce a sodium hydroxide solution. The pH of this solution would be 14, which shows it is an alkali.
sodium oxide + water ‚Üí sodium hydroxide
Base + water ‚Üí alkali
Non-metal oxides
Non-metal oxides are often gases. One of the properties of most non-metal oxides is that they dissolve in and react with water, producing solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water. which are acidicA word which describes substances with pH values lower than 7. . This means the solutions have pH values which are lower than 7.
For example, sulfur burns in oxygen to produce sulfur dioxide. If universal indicatorUniversal indicator is a special indicator that shows a different colour for each pH value. is squirted into the jar (containing the sulfur dioxide) it immediately turns red which shows a pH of 1.
This tells us sulfur dioxide is an acidic gas.
Find out more about the pH scale in this guide.
An oxide sample is tested and found to have a pH of 3. What type of element is present in the oxide?
A non-metal.
Non-metals produce oxides which are acidic. This means a property of non-metal oxides is that they have pH values lower than 7.
Metal oxides act as bases
Metal oxides act as bases. Bases are substances which can neutralise acids. When a base reacts with an acid it produces a salt and water.
acid + base ‚Üí salt + water
The specific salt produced depends on which acid and base react together.
For example, copper oxide is reacted with sulfuric acid. This produces the salt copper sulfate.
copper oxide + sulfuric acid ‚Üí copper sulfate + water
CuO + H‚ÇÇSO‚ÇÑ ‚Üí CuSO‚ÇÑ + H‚ÇÇO

Find out more about neutralisation reactions in this guide.
Working scientifically
Drawing apparatus
The steps to make copper sulfate crystals from copper oxide and sulfuric acid are as follows:
- Measure 25 cm³ of sulfuric acid using a measuring cylinder and pour into a beaker.
- Warm gently using a Bunsen burner.
- Add copper oxide and stir until it dissolves into the acid.
- Add more copper oxide until it no longer dissolves.
- Filter out the unreacted copper oxide.
- Pour the solution (copper sulfate) into an evaporating basin and place this on top of a beaker of water.
- Heat the beaker of water using a Bunsen burner until it boils. The steam from the boiling water will warm the evaporating basin containing the copper sulfate solution, causing water to evaporate from the solution. Stop heating when blue crystals start to form around the edge of the copper sulfate solution.
- Allow the mixture to cool. The crystals will get larger and the remaining water will evaporate.
A series of scientific diagrams can be drawn to illustrate this method.

Keep your diagrams simple.
Always use a sharp pencil and a ruler for your straight lines, and don’t forget to include labels to make your diagram clear.
The two parts of this experiment can be represented by scientific diagrams. Have a look at this scientific diagram showing how to filter the solution.
Now have a go at drawing a scientific diagram to represent the heating of the solution. Click below to reveal an example of a diagram to help you.
Find out more about drawing scientific apparatus in this guide.
Quiz
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Periodic table
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 6

- count2 of 6

- count3 of 6
- count4 of 6
