Key points
- Most materials that we use are mixtureWhen two or more compounds or elements are present without being chemically bonded together., and just a few are pure elements or pure compounds.
- In chemistry, a pure substance is a single substance made of only one type of particle.
- impurityA substance that consists of more than one element or compound. change the temperature at which a substanceMatter made of a fixed ratio of atoms with characteristic properties. melts and boils.
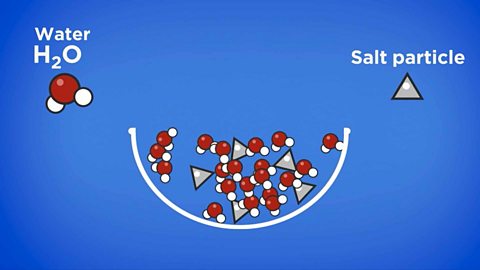
Cartons of fruit juice often say they contain ÔÇśpureÔÇÖ juice. Does the word ÔÇśpureÔÇÖ have the same meaning for a scientist as it does in everyday life?
In everyday life, for example on food packaging, the word ÔÇśpureÔÇÖ usually means that something is in its natural state without anything added to it, like sweeteners or preservatives. Natural fruit juice is made up of sugar, water and many other naturally occurring chemicals. In chemistry this is not considered 'pure' and is a mixture.
Video
Watch this video to find out about the difference between pure and impure substances.
Miss Fong: Today we're going to be looking at pure and impure substances and how we can test for purity.
First, let's cover the basics. A pure substance is made from only one compound or just one element with no other substances mixed in. Hold up those two glasses, Katie. Imagine the pompoms represent individual chemical atoms within a substance.Each glass contains pompoms of the same colour. So the substances would be classed as pure.
Katie: And impure is when this is the case where there is a mix of them.
Miss Fong: Correct. An impure substance is one which contains a mixture of elements, a mixture of compounds, or a mixture of both elements and compounds.
Katie: Whoo-hoo, this is fun. I think I'm starting to get it. But before we go any further, let's watch this handy infographic on pure and impure substances.
VOICEOVER: Pure and impure substances.
The word pure in everyday life doesn't have the same meaning in science.
For example, pure orange juice is a mixture of compounds and bottled water still has impurities. In science, the word pure means a substance made from one element or just one compound. Remember that a compound is made from two or more elements which are chemically bonded together.
Most substances contain impurities. But if the particles in these mixtures are not chemically joined, they can usually be separated using a physical process. Impurities can also change the properties of substances. Gritters spray salty grit onto roads in winter. This is because the salt lowers the freezing point of water, so it has to get even colder than zero degrees Celsius before it turns to ice. Brr!
Katie: So, Miss Fong, I've got a question for you. In my fridge I've got a carton of orange juice which says pure on it, so are the manufacturers bending the truth a little bit?
Miss Fong: No, not really. The manufacturers are using the word pure in its everyday meaning, which tells you that nothing has been added to the orange juice. We know that, chemically speaking, natural orange juice is a mixture of water, sugar, vitamins and other substances.
Katie: OK, so my juice is chemically impure, technically?
Miss Fong: Yes. It contains a mixture of elements and compounds. I'm going to test you on some other items now. Tell me if you think they're pure or impure.
Katie: All right, let's go for it. And you can play along at home, too.
Miss Fong: OK. First up, the air that we breathe.
Katie: Oh, surely the air that we breathe is impure because it's more than one gas.
Miss Fong: Correct. The air we breathe contains different elements and compounds, like nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, as well as trace amounts of others, like methane and nitrogen oxides. Next up, helium, like in these balloons.
Katie: Um, I would say that is pure because it's a single element.
Miss Fong: You're exactly right, Katie. Helium is a gas made up of a single element. Final one now, salt.
Katie: Oh, salt. I feel like I want to say that's impure because salt must be a mix of different things.
Miss Fong: No, salt is actually pure.
Katie: Ah.
Miss Fong: It only contains one compound, something called sodium chloride. As the two elements sodium and chlorine are chemically bonded together. They make a compound called sodium chloride and, as this is the only thing in salt, salt is pure.
Katie: That is fascinating stuff, Miss Fong. Thank you. I won't look at salt the same way again next time I'm sprinkling it on my fish and chips.
Miss Fong: Sticking with salt, I want to show you something else fascinating. Remember earlier, I said we could test for purity? We can do that with the help of some common table salt.
Katie: Which I miraculously now have in my hand.
Miss Fong: You've also got two pans there, each filled with one litre of distilled water.
Katie: OK, so if it's distilled water does that mean it's pure?
Miss Fong: Absolutely. If you could pour 60 grams of salt into just one of the pans.
Katie: OK.
Miss Fong: In the lab, you would then place both pans on a heat source and watch them to see when the water reaches their boiling points. This is not something to try at home. We have images on the screen. What do you notice?
Katie: Oh, OK. So, there's a difference. The distilled water is boiling at 100 degrees Celsius, while the temperature of the salty water is higher, boiling at around 102 degrees Celsius. Why that difference?
Miss Fong: Well, adding salt to water makes the water impure, so it takes longer to boil salty water, and the boiling point is higher too.
Katie: Wow, that's fascinating stuff. Thank you very much, Miss Fong.
Is the air that we breathe a pure or impure substance?
The air that we breathe is impure. It is a mixture of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and many impurities such as methane.
Pure substances

pureA substance of only one element or one compound. substances are made from only one chemical elementA pure substance which is made from only one type of atom. Elements are listed on the periodic table. or one compoundA pure substance made from two or more elements which are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. .
For example, salt is a pure substance made only of sodium chloride.


- Elements are listed on the periodic table
- Elements are made from one type of atomThe smallest particle of an element. We often think of atoms as tiny spheres, but in fact they are made from smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons.
- A compound is made from two or more elements bonded together
Can you name two examples of compounds?
Examples include pure water, which is HÔééO, and carbon dioxide, COÔéé.
Impure substances
Impurities
A substance made from more than one element or one compound is impure, meaning it is a mixtureWhen two or more compounds or elements are present without being chemically bonded together..

A label for a bottle of water will often include a list of small amounts of other substanceMatter made of a fixed ratio of atoms with characteristic properties.. These are called impurities.
For example, it is challenging to make pure water. This mineral water contains small amounts of impurityA substance that consists of more than one element or compound. such as sodium and nitrate.

Which of the following, if any, is a pure substance?
- Sea water
- Water in a mountain stream
- Distilled water in the school science laboratory
- None of the above
None of these examples is a chemically pure substance.
- Sea water is not pure because it is a mixture of water, salt, and other dissolved substances.
- The water in a mountain stream contains much less salt than sea water. It still contains some impurities, such as dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide, minerals and microorganisms.
- Distilled water contains very small amounts of impurities.
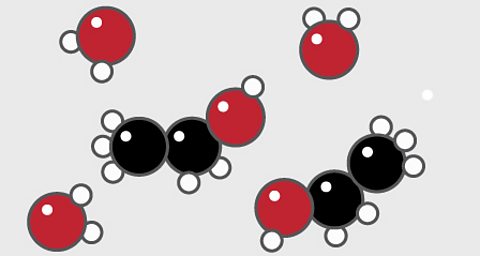
Particle diagrams
Particle diagrams are used to show how chemicals are arranged.
Elements
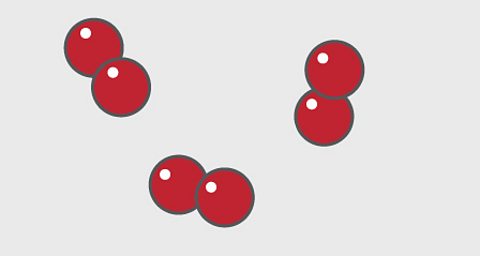
A particle diagram for an elementÔÇ»will have only one type ofÔÇ»atom.
For example, pure oxygen contains only oxygen atoms. Oxygen is shown here as a red circle.

Compounds
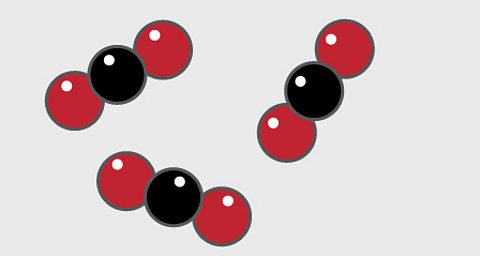
- A particle diagram for a compound will have two or more types of atom bonded together in aÔÇ»fixed ratio.
- The compound of carbon dioxide is made up of two types of atom, shown here as one red and one black circle. Carbon is shown as black and oxygen is red.
- The compound has a fixed ratio of one black atom joined to two red atoms.

Mixtures
A particle diagram for a mixture has more than one type of atom which are not chemically bonded together, or more than one type of molecule.
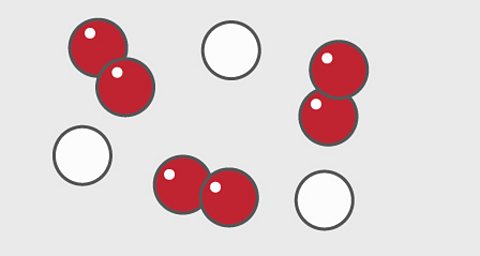
For example, this particle diagram shows helium in white and oxygen in red.
The two red atoms are joined together but not to the white atom, so this is a mixture of two elements.

Fixed boiling points
A pure substance has a fixed melting pointThe temperature at which a pure substance melts from a solid into a liquid. For example, the melting point of pure water is 0┬░C. The melting point is also the temperature at which a liquid will freeze to a solid. and boiling pointThe temperature at which a pure substance boils from a liquid into a gas. For example, the boiling point of pure water is 100┬░C. The boiling point is also the temperature at which a gas will condense into a liquid., which means they will always melt or boil at exactly the same temperature. For example, the melting point of pure water is 0 ┬░C and its boiling point is 100 ┬░C.
Impurities change the melting and boiling point
When a substance contains impurities, its melting and boiling points change. When salt is added to water, the mixture freezes below 0 ┬░C, and boils at a temperature over 100┬░C. However, It is possible to find out if a substance is pure or not by measuring its melting or boiling point.

Working scientifically
Using a thermometer
Here are some top tips for using a thermometer to measure the temperature of a substance.
Top tips
- Make sure that the bulb of the thermometer is covered by the liquid but not touching the bottom of the container.
- Give the thermometer enough time to reach the same temperature as the liquid youÔÇÖve dipped it into. Stir the liquid with the thermometer to make sure all the liquid has the same temperature.
- Watch the coloured liquid in the thermometer move. When it stops moving, it's ready to read.
- Hold the thermometer in the liquid and get down to read the temperature at eye levelIn line with your eyes..
Using a thermometer is a useful measuring tool for collecting data.
Find out more about collecting data in science.
Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Pure and impure substances
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 7

- count6 of 7

- count7 of 7

- count1 of 7