Key points
A sound wave is a vibration that travels through a solid, liquid or gas such as the air or water.
A loud sound has a large amplitude, a high pitched sound has a high frequency.
Musicians and scientists record and analyse sounds using wave traces.
How are sounds made?
When something shakes, scientists call it a VibrationVibration is the fast back and forwards movement of an object or particles.. All sounds are made by something that is shaking or vibrating.
Sometimes you can see the source of the sound vibrating, like a guitar string, drum or a loudspeaker, but other times it’s notso obvious, like the floor vibrating when you drop something on to it.
Watch this video to learn about what happens to sound waves when you record a song.
Jon Chase joins singer-songwriter Charlie-Anne Bradfield to find out about what happens to sound waves when you record a song.
What is a sound wave ?
You don’t hear a sound as soon as it is made. It takes time for it to reach you.
Click on the slide show below to see how a sound travels through the air to reach your ear.
How sound travels
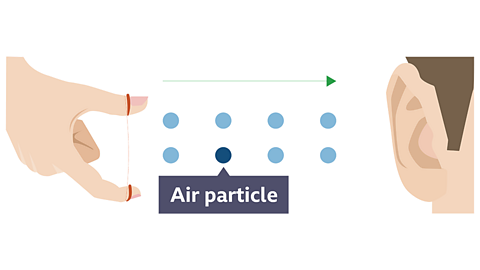
Image caption, When there is no sound the air particles are still.
Image caption, When you pluck the rubber band it pushes on the air particles next to it and sends them forwards.
Image caption, The first set of air particles hit the next set of particles and bounce back.
Image caption, Each set of air particles bounce back and forth passing on the vibrations to the next set of particles.
Image caption, When the particles next to your ear start vibrating you hear the sound.
1 of 5
When there is a sound wave, the air particles don’t travel directly from the object making the sound to your ear. Sound waves are vibrations being passed on between particles. In the example above, the vibrating rubber band pushes on the air particles next to it.
The air particles start vibrating and push on the air particles next to them, so the vibrations arepassed on. Look at one particle (for example, the dark blue one), although the particle moves back and forth, it doesn't actually go anywhere, it just passes the movement on.
The particle moves one way and then moves back in the opposite direction, so ends up back where it started.The particles vibrate in the same direction as the wave travels. Sound is an example of a longitudinal waveA wave where the particles move forwards and backwards in the direction that the wave travels. For example sound waves and the movement you get if you moved a metal spring forwards and backwards..
Loudness
If you pluck a stretched rubber band hard, it makes a loud sound. If you pluck it gently, it makes a quiet sound.
The loudnessLoudness is a measure of how humans hear sound intensity. It is measured in decibels (dB), a scale based on human hearing ability, and starts at 0 dB. of a sound depends on how big the vibration of the air is.
- If air particles move back and forth a lot we hear a loud sound.
- If the source of a sound makes the particles vibrate more gently, we hear a quieter sound.

Pitch and frequency
The more stretched a rubber band is, the quicker it vibrates and the higher the pitchThe pitch of a sound is how high or low the sound is. A high pitch sound has faster vibrations and higher wave frequency. A low pitch has slower vibrations and a lower wave frequency. of the sound.
The pitch of a sound depends on how quickly the air vibrates.
- When air particles move back and forth quickly we hear a high pitch sound.
- When the air vibrates less quickly we hear a low pitch sound.
The number of vibrations each second is called the frequencyFrequency is the number vibrations of the wave in one second, also seen as the number of complete waves passing a point in one second. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). and is measured in a unit called hertzFrequency is measured in hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz).. The lowest pitch sound that most humans can hear is 20 Hz. The highest pitch sound the average human can hear is 20,000 Hz. The pitch you can hear varies with your age.
Which animal has the highest frequency sensitivity?

Scientists have discovered that the greater wax moth is capable of sensing sound frequencies of up to 300,000 Hz (300 kHz), the highest recorded frequency sensitivity of any animal in the natural world.
Wave traces
To record or analyse a sound, scientists and musicians use a microphone to turn the sound into an electrical signal. The electrical signal can then be displayed on a device called an oscilloscopeA machine that shows the wave shape of an electrical signal upon a screen. and it produces a graph called a wave trace A graph that can be used to compare the pitch and loudness of a sound..
Wave traces
Wave traces appear on an oscilloscope graph as a transverse waveA wave in which the particles move up and down at right angles to the direction it travels in, like an ocean wave or lifting a rope up and down., but it is important to remember that because they are a sound, they are actually a longitudinal waveA wave where the particles move forwards and backwards in the direction that the wave travels. For example sound waves and the movement you get if you moved a metal spring forwards and backwards..
Wave traces are graphs that show how big the vibration of the air particles is on the vertical axisThe line on the graph that runs up and down, from the bottom to the top of a graph. Sometimes called the y axis. against the time on the horizontal axis The part of a graph that runs from left to right, think of it as a flat line, like the horizon. Sometimes called the x axis..
A loud sound makes the air move back and forth a lot and so the peaks on the graph are big. A quiet sound makes the air vibrate back and forth less, so the peaks are smaller.
A high pitch sound has a high frequency and makes the air vibrate quickly , so the wave peaks are closer together.
A low pitch sound makes the air particles vibrate more slowly and so the peaks are further apart.
On a wave trace:
- If there is no sound, the wave trace is a flat line.
- How high the peak of the graph is compared to the flat line is called the amplitudeThe height of the top of a wave from its resting position. The greater the amplitude, the taller the wave (and the louder the sound if a sound wave)..
- The higher the pitch the more peaks there are (the frequency of waves).
Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count12 of 15

- count13 of 15

- count14 of 15

- count15 of 15
