Key points
We can hear sounds because our ears turn sound vibrations from the air, into signals that are sent to our brain.
We can’t hear all levels of sounds. Sound waves with very high frequencies are called ultrasound and our ears can’t detect them.
Ultrasound waves have multiple uses including: detecting medical conditions, treating kidney stones and cleaning delicate objects.
How we hear
We detect sounds because inside our ears we have parts that work together to turn sound waves into a signal that is sent to our brain.
The components of the ear that make this possible are:
The eardrum: A thin flap of skin that is stretched tight like a drum.
The ear bones: Three small bones called the hammer, anvil and stirrup.
The cochlea: A spiral shaped part of the ear that looks a bit like a snail shell.
The auditory nerve: The nerve that carries signals from the cochlea to the brain.
The Pinna: The visible portion of the outer ear.
When a sound reaches us, the air particles inside our ear canalrefers to the tube that runs from the outer ear to the inner ear. Lined with cells that produce ear wax. vibrate and hit the eardrum.
The eardrum then starts vibrating and these vibrations are passed to three small ear bones – called the hammer, anvil and stirrup.
The stirrup bone hits the cochlea, which turns the vibrations into an electrical signal that is sent to our brain via the auditory nervethe auditory nerve carries messages from the cochlea to the brain..
When the signal reaches our brain, our brain translates the signal into the sound we hear.
Ultrasound
The highest pitchThe pitch of a sound is how high or low the sound is. A high pitch sound has faster vibrations and higher wave frequency. A low pitch has slower vibrations and a lower wave frequency. sound humans can hear has a frequencyFrequency is the number vibrations of the wave in one second, also seen as the number of complete waves passing a point in one second. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). of 20, 000 hertzFrequency is measured in hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz).(20 kHz). If the vibrations of a sound wave have a frequency that is higher than 20 kHz our ears can’t detect them and it is called Ultrasound Sound waves which we can’t hear because they have a high frequency of more than 20, 000 Hz. .
- If the vibrations of the air particles are slower, we hear a lower pitch sound.
- If the vibrations of the air particles are faster we hear a higher pitch sound.

Many animals have ears that are able to detect ultrasound. Dogs are able to hear sounds with frequencies up to 60 kHz, while some species of bats can detect frequencies of 200 kHz.
A dog training whistle makes sound waves that have a frequency of 40,000 Hz. Dogs ears can detect the sound, humans can’t because the frequency is above 20 kHz.
What is a Mosquito alarm used for?
In 2005, Howard Stapleton from Barry in South Wales invented the Mosquito alarm. It is a device that makes a noise at a frequency of 17.4 kHz.
It was found that younger people, including teenagers and young adults could hear this pitch and were irritated by it, however older people, whose ability to hear higher pitch has lessened with age, were oblivious to the sound. These devices were deployed all over the world in order to prevent loitering, vandalism and drug use outside properties and shops.
Uses of ultrasound
Even though we can't hear ultrasound, it has many other uses for humans.
Breaking kidney stones
Ultrasound waves can move physical objects by resonating with their natural frequency and are used by doctors for breaking up kidney stonesKidney stones happen when minerals form crystals inside the kidneys. Then they get bigger and become kidney stones. Kidney stones can move into the urinary tract. There, they can cause problems like pain and blood in the urine. .
Watch the video below to see how sound travels through, and affects, different materials.
How can sound waves be used to treat kidney stones and to smash wine glasses?
A glass will smash if sound waves travel through it at what frequency?
A glass will smash if sound waves travel through the glass at its natural frequency. In the example in the video that is around 550 hertz.
Cleaning delicate objects
Ultrasound can be used to clean delicate objects like jewellery or a pair of glasses. The machines that make use of this ability are called ultrasonic cleaners.
When the ultrasonic cleaner is switched on, ultrasound waves travel through the water, disturbing it and creating tiny bubbles that vigorously shake the dirt from the object.

Looking inside the body
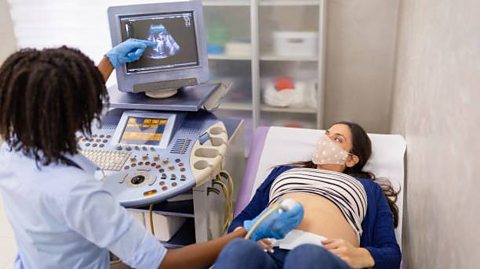
Ultrasound scans are used to view the inside of our bodies. A small device called an ultrasound probe is used, which gives off high-frequency sound waves.
We can't hear these sound waves, but when they reflect off different parts of the body, they create echoes that are picked up by the probe and turned into an image called an ultrasound scan.
Low power ultrasound is used so that doctors can see images of inside the body without causing damage. Ultrasound waves are used to take pictures of unborn babies, to monitor vital organs such as the heart, or to assist in diagnosis of gall or kidney stones.
Checking for faults inside objects
Ultrasound waves are used to check if railway tracks and oil pipes have hidden faults, like a crack inside that is not visible to the naked eye. The waves are aimed at the surface and their reflections are received by a probe. If there is a crack or fault, the ultrasound wave reflects differently from how it does when there isn't a fault, and the probe produces a different noise to indicate that a fault has been found.

Test your knowledge
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count14 of 15

- count15 of 15

- count1 of 15

- count2 of 15
