Multicellular organisms
Producing new cells
Cell division allows for growth and replacement of dead cells. Most multicellular organisms are made of different cell types that are specialised to carry out specific functions.

Control and communication
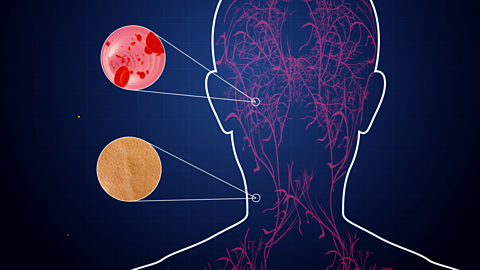
Communication between cells in a multicellular organism occurs by use of nerve impulses or hormones. The central nervous system produces electrical impulses for rapid response.
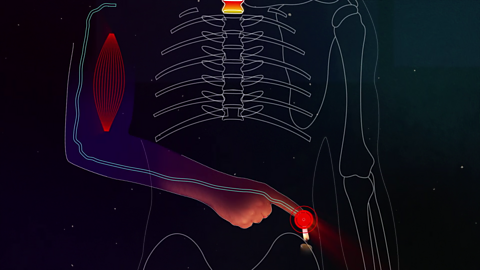
Reproduction
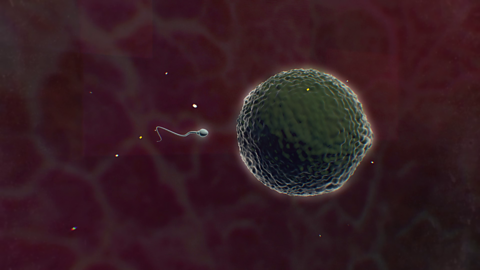
New organisms are produced when male and female haploid gametes fuse. In mammals, gametes are produced in the testes or ovaries of individuals but anthers and ovaries are on the same flowering plant.
Variation and inheritance
The phenotype for a characteristic like eye colour is the result of the combination of alleles. If the alleles in the parental genotype are dominant or recessive, probable outcomes can be predicted.

Transport systems - Plants
Multicellular organisms require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. Plants transport substances through xylem and phloem.

Transport systems - Animals
Multicellular organisms require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. The heart uses blood vessels to transport these substances around the body.
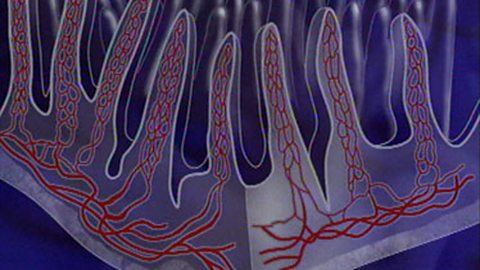
Absorption of materials
Humans require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs and food molecules are absorbed by the digestive system.

Video playlist
Specialised and non-specialised cells. Video
Comparing the roles of specialised and non-specialised cells in both animals and plants.
The digestive system. Video
Animated description of the digestive process and the structures of the digestive system.
Sexual reproduction in animals. Video
The biological processes involved in the sexual reproduction of animals.

Plant and animal cell structures. Video
A look at the cells of different organisms and a comparison of structures.
Van Helmont's experiments on plant growth. Video
How Jan Baptist van Helmont showed that plants did not use soil to grow.

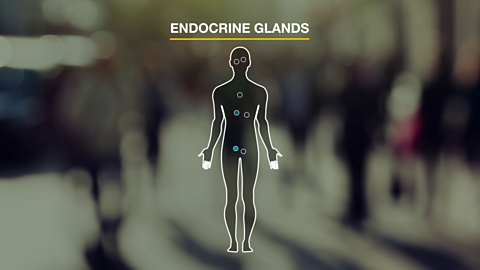
Hormonal systems. Video
Endocrine glands produce hormones that regulate conditions in the body.
Skeletal muscles. Video
Looking at the role of skeletal muscles in moving parts of the body.

Nervous system. Video
The nervous system controls how the human body responds to sensory information.

A balanced diet. Video
An explanation of balanced diet and amounts of the food groups that make it up.

Transport and exchange - Digestive system. Video
Food is broken down and absorbed as it moves through the digestive system.

Genetics. Video
Genetic information in an organism's DNA controls its phenotype.

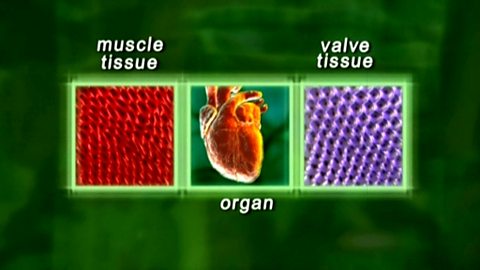
The difference between cells, tissues and organs. Video
An explanation of how cells make up tissues which in turn make up organs.
Transport and exchange - Gas exchange. Video
The movement and exchange of gas through the respiration system in animals.
Transport and exchange in plants. Video
The movement of water, nutrients and gases through a plant.

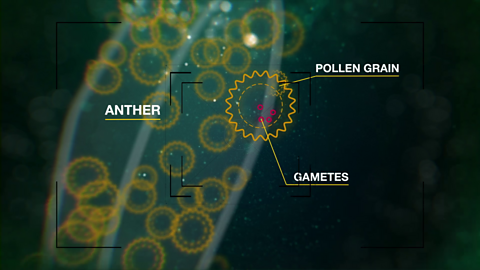
Sexual reproduction in plants. Video
Sexual reproduction involves haploid gametes fusing to form a diploid zygote.
Reproductive cycle of crabs. Video
Professor Richard Fortey investigates the reproductive cycle of the crab.

Transport and exchange - Blood circulation. Video
The heart pumps blood around the body. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients.
Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link