Cell biology
Cell structure
Cells are microscopic building blocks of unicellular and multicellular living organisms. Animal, plant, fungal and bacterial cells are different in terms of structure but also have many similarities.
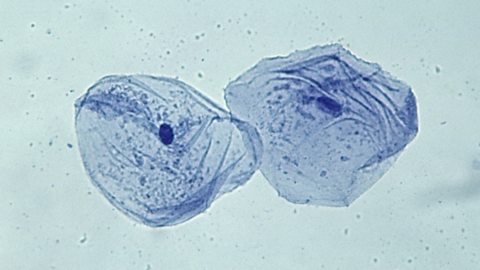
Transport across membranes
All cells are enclosed by a cell membrane, which is selectively permeable. Molecules can move into or out of cells by diffusion and active transport. Cells can gain or lose water by osmosis.

DNA and the production of proteins
DNA carries the genetic information in the cells of all living organisms. It contains codes for the assembly of amino acids into all the proteins required in the body.

Proteins
Proteins consist of combinations of amino acids. Body proteins include structural proteins, enzymes, hormones and antibodies. The shape of an enzyme allows it to speed up a biological reaction.

Genetic engineering
Bacteria exchange DNA using plasmids; viruses invade cells by first inserting their genetic material. Genetic engineering is the transfer of DNA between organisms using biotechnology.

Respiration
Most cell activity requires chemical energy. Respiration is the cellular process of releasing energy from food and storing it as ATP.
- 7 videos

Multicellular organisms
Producing new cells
Cell division allows for growth and replacement of dead cells. Most multicellular organisms are made of different cell types that are specialised to carry out specific functions.

Control and communication
Communication between cells in a multicellular organism occurs by use of nerve impulses or hormones. The central nervous system produces electrical impulses for rapid response.
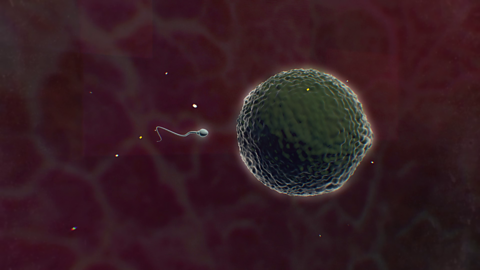
Reproduction
New organisms are produced when male and female haploid gametes fuse. In mammals, gametes are produced in the testes or ovaries of individuals but anthers and ovaries are on the same flowering plant.
Variation and inheritance
The phenotype for a characteristic like eye colour is the result of the combination of alleles. If the alleles in the parental genotype are dominant or recessive, probable outcomes can be predicted.

Transport systems - Plants
Multicellular organisms require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. Plants transport substances through xylem and phloem.

Transport systems - Animals
Multicellular organisms require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. The heart uses blood vessels to transport these substances around the body.
Absorption of materials
Humans require transport systems to supply their cells and remove waste products. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs and food molecules are absorbed by the digestive system.

- 17 videos
Life on Earth
Ecosystems
An ecosystem is a community of animals, plants, micro-organisms, non-living things and their shared environment. Find out about energy transfer, niches and competition in ecosystems.

Distribution of organisms
Abiotic factors are non-living variables. Biotic factors are the interactions between organisms. Both affect diversity and distribution. Sampling helps us to estimate numbers of organisms in an area.

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants use sunlight energy to make their own food. It takes place inside the chloroplasts of plant cells.

Energy in ecosystems
All organisms require energy. The feeding relationship in an ecosystem can be shown in a foodchain. Learn about pyramids of biomass, energy and numbers.

Food production
A growing human population demands increased food production. Farmers try to meet that demand by intensive farming, using fertilisers and pesticides that are impacting on the environment.

Evolution of species
Mutations can alter the genes of individuals in a beneficial or detrimental way and introduce variety into a species.
Apparatus and techniques
There is a range of apparatus that National 5 Biology students must have knowledge of. The course also involves being able to describe and carry out experimental and measuring techniques.
- 14 videos
Exam and assignment
Exam skills
Exam skills advice for National 5 Biology

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link