Fungal diseases
Not all fungiA large group of eukaryotic organisms that contain single-celled yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. cause diseaseIllness affecting plants and animals.. yeastA unicellular fungus used in the brewing and baking industries. is a single-celled fungus that is economically important because we use it to make things like bread and beer. Not all fungi are single-celled. Some such as mushrooms are multicellular and so much larger. These are still made of tiny cells like yeast, but have many more of them. Fungal cells have a nucleusThe nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. and so are eukaryoticDescription of a cell which has a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells also have other structures in the cytoplasm which have membranes around them..
Athlete's foot
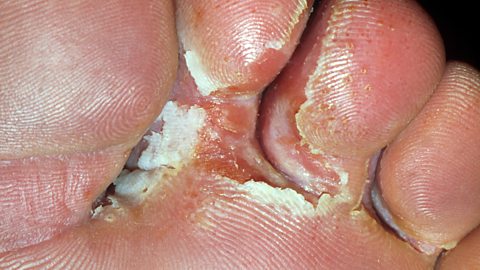
athlete's footA rash caused by fungus growing on feet that can be treated by antifungal medication. is a rash caused by a fungus that is usually found between people's toes. It causes dry, red and flaky or white, wet and cracked skin. It is often found in communal areas like swimming pool changing rooms or gyms. It is transmitted by touching infected skin or surfaces that have been previous contaminated. It is treated by antifungal medicationDrugs that treat fungal infections like athlete's foot..
Chalara ash dieback
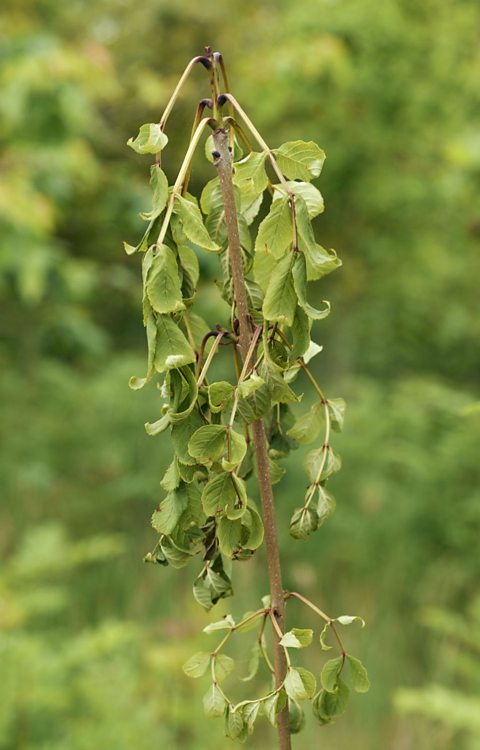

A species of fungus called Hymenoscyphus fraxineus infects ash trees. Infected plants suffer the following symptoms:
- leaf loss
- die back of new shoots
- bark lesions.
This species of pathogenic fungus is relatively new to the UK. The fungus spreads through the air, so we call it an airborne infection. Since 2012 it has spread to about one third of all large woodlands in the UK.
Scientists are not yet sure how quickly this fungus will spread of what its full impact will be on our ash population. They are trying to identify the genetic factors that mean that some ash trees are naturally resistant to the fungus.