Health, disease and the development of medicines
Communicable disease - Edexcel
Disease-causing viruses, bacteria, fungi or protists are called pathogens. Sterilising water, preparing food hygienically, washing, vaccination and barrier contraception can reduce the spread of pathogens.
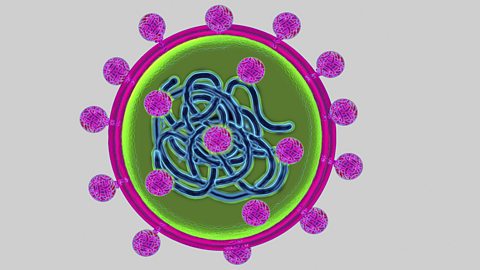
Plant disease - Edexcel
Pathogens are disease-causing viruses, bacteria, fungi or protists. Some pathogens infect plants and others infect animals. Plants have physical and chemical defences against pathogens.

Treating, curing and preventing disease - Edexcel
The immune system defends humans from pathogens. Physical and chemical barriers prevent infection. White blood cells attack pathogens. Immunisations usually involve injecting inactive pathogens.

Making medicines - Edexcel
The development of drugs is a long, complicated and expensive process. Monoclonal antibodies are identical copies of an antibody. They are used in pregnancy tests and in cancer treatment.
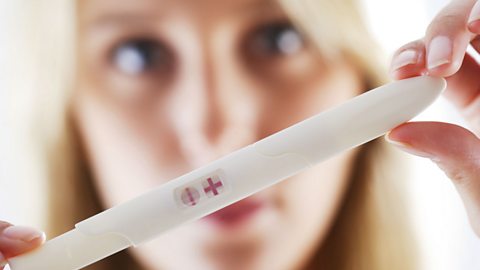
Non-communicable diseases - Edexcel
Non-communicable diseases are not transferred between people, eg cancer, diabetes, genetic and neurological disorders and heart disease. Risk factors increase the chances of developing these diseases.
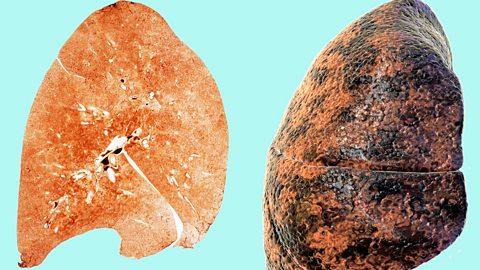
Sample exam questions - health, disease and medicine development
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription