Life in Nazi Germany, 1933-45
Hitler takes political control 1933-1934 - CCEA
Revise the events which lead to Hitler's control of Germany including the Reichstag Election, the Enabling Act and how opposition was eliminated.

Control and opposition in Nazi Germany - CCEA
In order to maintain his absolute power, Hitler needed to ensure the total loyalty of the people to him.

Life for workers in Nazi Germany - CCEA
Hitler aimed for full employment and self-sufficiency for German people through a variety of methods.

Life for women and the family in Nazi Germany - CCEA
Women were to serve and nurture their family while men were in charge and had to protect their family. Hitler said this was "the natural order".

Life for young people in Nazi Germany - CCEA
Young people were very important to the Nazis. To this end, Hitler set about influencing children both inside and outside school.

Life for the Jewish community and minorities in Nazi Germany - CCEA
Hitler and the Nazis had firm views on race, believing Germans were the Master Race. Others were categorised as slave races and sub-human.

Life in Germany during World War Two - CCEA
Germans reacted to the outbreak of the World War Two with resignation and feared a repeat of the shortages and huge loss of life of World War One.

Life in the United States of America, 1920-33
Life for black Americans - CCEA
The USA Constitution states that everyone is equal, but many groups such as black Americans were not treated fairly (CCEA).

Life for immigrants - CCEA
At the end of the nineteenth century, the USA had an Open Door policy which encouraged immigration.

Life for Native Americans - CCEA
The 1920s was an era of discrimination against the Native Americans.

Prohibition - CCEA
On 16 January 1918, the Eighteenth Amendment to the USA’s Constitution made it illegal to manufacture, transport and sell alcohol in the USA.

Social change and popular entertainment - CCEA
The 1920s was a period of great cultural and social change in the USA.

The ‘Roaring Twenties’ - CCEA
The 1920s was a period of rapid change and economic prosperity in the USA.

Economic problems in the 1920s - CCEA
Weaknesses in the American economy became more apparent as the 1920s progressed.

The Wall Street Crash, 1929 - CCEA
On Black Tuesday, 29 October, 16 million shares were sold on the Stock Market in Wall Street and the US economy collapsed completely.

The Great Depression, 1929-1933 - CCEA
In October 1929, the Roaring Twenties came to a dramatic end and the USA economy went into deep depression.

Changing relations: Northern Ireland and its neighbours, 1920-49
The partition of Ireland - CCEA
Until the beginning of the 1920s Ireland was ruled directly by Britain. However, not everyone was happy that the British controlled the island.

From Irish Free State to Éire - CCEA
How did Éamon de Valera go about dismantling the Anglo-Irish Treaty?

The Economic War, 1932-1938 - CCEA
In 1932, the Irish Free State and Britain began what became known as the Economic War which had far-reaching consequences for them and for Northern Ireland.

Northern Ireland and World War Two - CCEA
World War Two had a profound impact on Northern Ireland.

Éire’s neutrality and its impact on relations during the war - CCEA
In April 1939, de Valera made it clear he would keep his country out of any potential war.
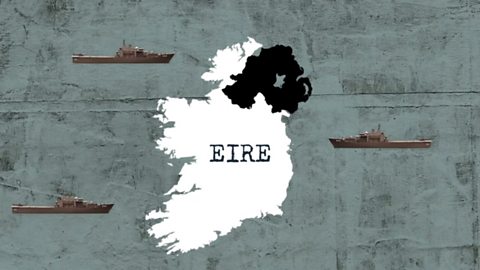
Impact of German attacks on Britain, Northern Ireland and Éire - CCEA
By June 1940, Hitler began planning Operation Sealion which was the invasion of Britain and this would have huge implications for Northern Ireland and Éire.

Life in post-war Northern Ireland and Éire - CCEA
After World War Two, there was a sharp contrast in life for those living in Northern Ireland compared to Éire.

Constitutional change in Éire and its effects - CCEA
What was the effect of constitutional change in Éire on its relationships with Britain and Northern Ireland?

Changing relations: Northern Ireland and its neighbours, 1965-98
The O'Neill years - CCEA
When Terence O’Neill became Northern Ireland’s Prime Minister in March 1963, he wanted to heal the 'ancient hatreds' that divided the two communities.

The campaign for civil rights - CCEA
The Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA) was formed in 1967 and began campaigning for reforms in voting rights, housing allocation and policing.

Violence in 1969 - CCEA
By 1969, the situation had become so tense that it looked as if violence would break out at any time.

The re-emergence of paramilitary organisations - CCEA
The re-emergence of paramilitary groups within Northern Ireland’s two communities threatened any prospect of a peaceful end to the tensions that had been developing.

Internment: Reasons, actions and effects - CCEA
By 1971, the new Prime Minister of Northern Ireland, Brian Faulkner, decided to try out an old method of dealing with paramilitary violence.

Direct Rule, 1972 - CCEA
The Stormont government was not able to deal with the deteriorating security situation. British Prime Minister Edward Heath decided it was time for his Government to get involved.

Power-sharing 1973-1974 - CCEA
With Stormont closed down, the British Government decided that it had to try out a very different solution if peace was to be restored to Northern Ireland.

Changing republican strategy 1980-1981 - CCEA
The decision of the British Government to introduce new security policies in the late 1970s had an impact on the ‘Troubles’ that was never predicted.

Anglo-Irish Agreement, 1985 - CCEA
The London and Dublin Governments decided that it was time for them to act to halt the rise of Sinn Féin.

The Downing Street Declaration, 1993
In December 1993, the British and Irish governments produced the Downing Street Declaration which outlined their approach to peace.

The Good Friday Agreement, 1998 - CCEA
What led to the Good Friday Agreement and what were its terms?

International relations, 1945-2003
Co-operation ends and the Cold War begins - CCEA
How did the collapse of the 'Grand Alliance' lead to the Cold War?

Emerging superpower rivalry and its consequences, 1945-49 - CCEA
As the Second World War came to an end, the growth of the Soviet superpower became increasingly apparent in Eastern Europe.

The Berlin blockade and airlift - CCEA
What caused the Berlin blockade crisis of 1948?

The Hungarian uprising - CCEA
A public uprising in Hungary against the USSR lead to bloodshed. What caused it? And what was the effect on international relations?

The Berlin Wall - CCEA
Learn about the reasons for growing tension over Berlin, the response of the West, the building of the Berlin Wall, and the consequences and impact on relations.

The Prague Spring - CCEA
For four months in 1968, Czechoslovakia broke free from Soviet rule. This period is now referred to as the Prague Spring, but why didn't it last?

The Korean War - CCEA
In June 1950, with the support of China and the Soviet Union, North Korea launched an attack on South Korea across the 38th parallel.

The Cuban Missile Crisis - CCEA
For 13 days in October 1962, the world appeared to stand on the brink of nuclear war. How was the Cuban Missile Crisis probably one of the most dangerous periods of the Cold War?

The Vietnam War - CCEA
How did Vietnam become a disastrous flashpoint for the US during the Cold War?

The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan - CCEA
After a period of détente between the US and the USSR, relations deteriorate once more over Afghanistan.

The end of the Cold War, 1985–91 - CCEA
The Cold War ended because of problems faced by the USSR and USA at home and abroad.

9/11 and the 'war on terror' - CCEA
The new age of conflict, the ‘war on terror’ and the impact on international relations.

The invasion of Iraq, 2003 - CCEA
The American invasion of Iraq in 2003 is partially seen as a legacy of the 1991 Gulf War.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link