What is glacial deposition?
Glaciers are massive rivers of ice that move across land. When they melt, they deposit materials which can create landscape features.
In this article you can learn:
- What glacial deposition is
- How a kettle hole is formed
- What an erratic is
- How a moraine is formed
- Different features of the Cairngorms National Park
This resource is suitable for Landscapes topics for primary school learners.
Video - Glacial deposition
Join Isla and Connor explore features of glacial deposition at Cairngorms National Park.
Watch this short video to find out about features of glacial deposition.
CONNOR: I can’t believe we can relax on the beach and ski a snow-capped mountain all in one National Park.
After climbing to the snowy plateau of Cairn Gorm it’s nice to chill here for a bit.
ISLA: Yeah, what a place the Cairngorms are!
And just like we can thank glaciers for snow-filled corries, arêtes and pyramidal peaks high up in the mountains, we can thank them for this beach! Loch Morlich is a kettle hole, a feature of glacial deposition - that's when a glacier drops things and leaves them behind.
Around 10,000 years ago when the last ice age was ending and the ice melted, glacial deposits were left behind.
When ice is melting, materials like sand, stones and rocks that have been carried along by the ice separate out into layers and are deposited in the melt water.
Kettle holes may be found if a block of 'dead ice' is partially buried by deposits. When the ice melts, a hole is left which may fill with water to form a kettle hole lake.
CONNOR: Ah, all we need now is the tropical weather. Although the sand feels a bit different from other beaches.
ISLA: That’s because it is a bit different to the sand by the sea. This is a mix of sand, silt, clay and gravel, deposited or left behind by glaciers travelling through the valley.
CONNOR: Works for me!
ISLA: Don’t get too comfortable! I want to look at some more kettle holes.
Here they are, the Uath Lochans Kettle Holes.
They were formed in the same way as Loch Morlich - by a giant chunk of ice which was part of the Strath Spey Glacier. It was over one kilometre thick!
When it began to melt it would have looked like a watery moonscape here. Huge chunks of ice half buried in sand and gravel. One of the ice chunks ended up where the lochans are, and melted so that the kettle holes became lakes of milky meltwater.
CONNOR: I bet the landscape looked really strange then - but there are still strange parts of the landscape today. Look at this huge boulder! It’s like it’s come out of nowhere.
ISLA: Yeah, what is it?
CONNOR: It’s an erratic. Erratics are large and unusually shaped rocks or boulders that are often found on their own, rather than in piles, and are made of a rock type not normally found in the area that they have been deposited.
All glacial deposits are angular and a mix of different rocks and materials dragged along from other places along the glacier’s path. Erratics are a good example of this.
ISLA: Yeah, it looks so dramatic up here! Imagine how powerful a glacier must be to carry this.
CONNOR: Yes, they really shape the landscape, leaving dramatic features like moraines.
Moraines are narrow ridges or hills. They’re made by the glacier bulldozing the land as it moves along its path, pushing everything it's carrying - dirt, rocks and debris. These are deposited along the way leaving ridges or hills - the moraines.
They can either be lateral - which means they form at the side of the glacier - or terminal, when they form at the end. Sometimes you also find erratics, those large boulders that are totally out of place!
ISLA: It’s not surprising that people made up all sorts of wild stories to explain how these rocks got here - but the glacier definitely makes more sense than giants throwing rocks at each other or being left here by UFOs!
CONNOR: Left here by UFOs? They’d have to be pretty strong to lift this!
ISLA: Stronger than you, that’s for sure!
CONNOR: I don’t know, I reckon I can shift it. Yeah, it definitely moved.
ISLA: Yeah right!
What is a glacier?
- A glacier is a huge mass of ice that moves slowly across land.
- A moving glacier can erosionWearing away over time. the land and create features of glaciated erosion such as corries, arêtes and pyramidal peaks.
As well as eroding the land, moving glaciers also create interesting landscape features through depositionWhen a glacier melts, the meltwater does not have enough energy to carry material, like sand and gravel, so it is dropped or dumped in the surrounding area..
Glacial deposition
- During the Ice Age, slow moving glaciers moved across land carrying materials, like sand, stones and rocks.
- By the end of the Ice Age (about 10,000 years ago) the glaciers were melting.
- When ice melts, material that has been carried along by the ice separates out into layers and is dropped, or depositionWhen a glacier melts, the meltwater does not have enough energy to carry material, like sand and gravel, so it is dropped or dumped in the surrounding area., in the meltwater.
What is a kettle hole?
- Large chunks of dead ice can become partly buried by these deposits of sand and gravel. When the ice melts, a kettle hole is left behind.
- Kettle holes may fill with water to form a kettle hole lake, like Loch Morlich and the Uath Lochans kettle holes.
- The sand found around kettle hole lakes is different from sand on a beach by the sea. This sand has been deposited by glaciers and is made up of sand, silt, clay and gravel.
How a kettle hole lake is formed
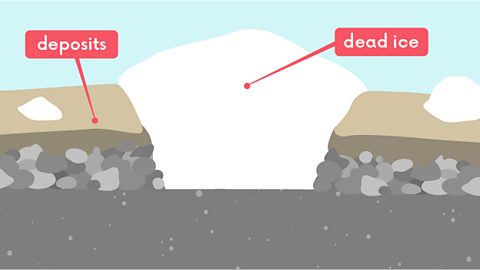
Image caption, 1. A large chunk of ice becomes partly buried by deposits of sand and gravel.
Image caption, 2. The ice melts and a kettle hole is left behind.
Image caption, 3. The kettle hole fills with water forming a kettle hole lake.
Image caption, Loch Morlich
Loch Morlich in Glenmore Forest Park, Cairngorms National Park, is a kettle hole lake. A chunk of ice from a glacier was buried in the land then melted leaving a hole behind. This hole filled with water becoming a loch. (imageBROKER / Alamy Stock Photo)
Image caption, Uath Lochans
Uath Lochans near Kingussie in the Cairngorms National Park showcases a great example of kettle hole lakes. Uath Lochans means the hawthorn small lochs. (Jim Laws / Alamy Stock Photo)
1 of 5
What are erratics?

- Glaciers can also carry and deposit large and unusually shaped rocks and boulders called erratics.
- Erratics are often found on their own rather than in piles.
- They are often made of a rock type not normally found in the area. Erratics are a mix of different rocks and materials dragged along from other places along the glacier's path.

What is a moraine?

A moraine is a narrow ridge or hill formed by dirt and rocks that have been pushed along by a moving glacier.
There are two main types of moraine:
- a Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. moraine which has formed along the sides of a glacier
- a Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. moraine which has formed at the end of a glacier


Key words about glacial deposition
- glacier - A massive river of slow moving ice.
- glacial features - Landscape features that have formed by glaciers.
- glacial deposition - When a glacier drops materials, like rocks and stones, and leaves them behind.
- Ice Age - A long period of time when the Earth's temperature became very low. The Earth's surface was buried under sheets of ice.
- kettle hole - A hole formed when a glacier gets stuck and buried in sand and gravel. When the ice melts, the kettle hole is left behind.
- kettle hole lake - A kettle hole that has filled with water.
- erratic - Large and unusually shaped rocks or boulders deposited by a glacier. They are often found on their own and are made from a rock type which is not usually found in the area.
- moraine - A narrow ridge or hill formed by dirt and rocks that have been pushed along by a moving glacier. They can be lateral (formed at the side of a glacier) or terminal (formed at the end of a glacier).
Exploring Cairngorms National Park
Cairngorms National Park in the Scottish Highlands is the largest national park in the UK. This huge park is packed with mountains, forest paths, rivers, lochs, unique wildlife, and villages.
Look at this map to see where Cairngorms National Park is and some of its main places and features.
Cairngorms National Park with Braemar Primary School
Explore more features of the Cairngorms National Park with The LAB and Braemar Primary School.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Challenge

Create a leaflet about one of Scotland's national parks.
A national park is an area set aside by government to preserve the natural environment. There are two national parks in Scotland:
- Cairngorms National Park
- Loch Lomond and the Trossachs
Research one of the national parks and design a leaflet.
Ideas to get you started:
- Where is the national park? Can you draw a map to show its location?
- Can you list some of its key features? Are there unique forests, mountains or lochs in the park?
- If you need help making your leaflet, learn more here: How to create a leaflet
Balmoral Castle. videoBalmoral Castle
Balmoral Castle sits just to the south of the River Dee in the Cairngorms National Park. Find out about the castle's Royal connection.

Forests. revision-guideForests
Isla and Connor explore forest in Loch Lomond and the Trossachs National Park.

Find out more about the landscapes in the Cairngorms National Park.

More on Landscapes
Find out more by working through a topic
- count17 of 25

- count18 of 25

- count19 of 25

- count20 of 25

