Key points
A parallel circuit is way of connecting components on separate branches, so the current can take different routes around the circuit.
Electrical circuits can be connected in parallel or in seriesA way of connecting components in a circuit. A series circuit has all the components in one loop connected by wires, so there is only one route for current to flow. .
The current is different in different parts of a parallel circuit.
The total resistance (R)How difficult it is for current to flow. in the circuit decreases when components are added in parallel.
The potential difference (V)The amount of energy transferred by each unit of charge passing between two points of a circuit. The unit for potential difference is the volt (V). is the same across all branches of a parallel circuit.
Game - series and parallel circuits
Play an Atomic Labs experiment exploring different arrangements of series and parallel circuits.
You can also play the full game
Video - Parallel circuits
In most buildings, the lights and sockets are all connected in big circuits but you can switch individual devices off, without affecting the others. Because, unlike a simple string of lights in a series circuit, these are all arranged in a parallel circuit.
And you can think of a parallel circuit as having several different routes that all run alongside, or parallel to, each other.
This simple circuit is like a one-bulb version of a building’s lighting circuit.
In a parallel circuit, if you want to add more bulbs, you add them on their own branches of the circuit, like this.
These new bulbs appear just as bright. That’s because each branch has the same voltage across it, and only has the resistance of one bulb.
Placing ammeters at different points in the circuit shows how the current is shared between the branches. It’s nought point nine amps here, and nought point three amps here, here and here.
Also, because each of the routes has its own current running through it, if we remove one of the bulbs, the others stay lit.
So, parallel circuits are really useful when you want your devices to keep working when one breaks or is removed. Like this!
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
What happens when you add a second bulb to a parallel circuit?
What happens when you remove a bulb from a parallel circuit?
Both bulbs will shine as brightly because each branch of the circuit has the same voltage across it but only the resistance of one bulb.
The other bulb (or bulbs) will stay lit, because there are still complete paths for current to flow to the other bulbs.
Connecting components in parallel
When we connect componentA part of a circuit eg a battery, motor, lamp, switch or wire. in parallelA way of connecting components in a circuit. A parallel circuit has components on separate branches, so the current can take different routes around the circuit., the components are connected on different branches of the circuit. There are two or more 'loops’ and multiple paths for a ł¦łÜ°ů°ů±đ˛ÔłŮĚý(±ő)Current is a flow of charges. It is measured in amps (A). to flow.
In a parallel circuit, if a lamp breaks or a component is disconnected, the other components continue working. This is because current continues to flow along remaining paths in the circuit.
Switches
Switches can be added to a parallel circuit to turn components on and off.
The position of switches in parallel circuit is important. If the switch is open, both lamps are off. When the switch is closed, both lamps are on.
Have a look at the slideshow to understand how adding switches can affect components in a parallel circuit.
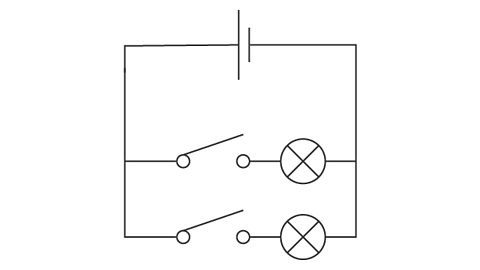
Image caption, Both switches are open and both lamps are off.
Image caption, The top switch is closed and the top lamp is on. The bottom switch is open and the lamp is off.
Image caption, The top switch is open and the top lamp is off. The bottom switch is closed and the bottom lamp is on.
Image caption, Both switches are closed and both lamps are on.
1 of 4

Parallel circuits are often used in homes. It allows individual devices to be controlled using switches. You don’t have to have all your devices switched on at the same time!

Current and resistance in parallel circuits
The current can have different values in different parts of a parallel circuit. This is because there are multiple paths for current to flow.
The current is shared between the different branches of the circuit
when current reaches a junction in the circuit, it splits up and some current flows along each route
when two branches of a circuit meet, the current combines again
the total current flowing through the cell can be found by adding the individual currents flowing through each branch.

Ammeters are used to measure current. Current is measured in amperes (A). The word 'amperes' is often abbreviated to 'amps'.
Resistance in parallel circuits
Unlike a series circuit, adding more components to a parallel circuit decreases the total resistance (R)How difficult it is for current to flow. of the circuit. Connecting more components into the circuit in parallel causes more current to flow through the cell, not less.
Identical lamps have the same resistance. Each lamp in parallel has the same current passing through it. Each lamp glows with the same brightness.
If the components in a parallel circuit have different resistances, a different amount of current will flow through each branch.
The greater the resistance of the component, the less current will flow through it. The current is still shared between the branches, and it still adds where the branches meet.
This parallel circuit contains a resistor and a lamp. A current of 5 A flows through the cell. The current splits at the junction.
3 A flows through the resistor and 2 A flows through the bulb.
The total current into a junction equals the total current out of a junction.
5 A = 3 A + 2 A.
More current flows through paths with lower resistance. More current flows through the resistor, so it must have a lower resistance than the lamp.
Potential difference in parallel circuits
In a parallelA way of connecting components in a circuit. A parallel circuit has components on separate branches, so the current can take different routes around the circuit. circuit, the potential difference (V)The amount of energy transferred by each unit of charge passing between two points of a circuit. The unit for potential difference is the volt (V). across each branch of the circuit is the same as the potential difference produced by the cell or battery. The potential difference is not shared between the components (like in a series circuit).
If a second lamp is added in parallel, it also has the same potential difference across it is - the full potential difference produced by the cell. This means the same current flows through each lamp, and they both glow just as brightly.
Quiz - Multiple choice
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Electricity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count11 of 11

- count1 of 11

- count2 of 11

- count3 of 11

