The Golden Age of Islam

During the Abbasid Caliphate (AD750 -1258), Baghdad became the centre for science, medicine, maths and more!
This early Islamic period is sometimes called the Golden Age of Islam because there were so many inventions in science and the arts at this time.
Why was the early Islamic civilisation a centre of inventions?
- The Abbasid caliphs (leaders) wanted people to learn.
- The city of Baghdad was home to a number of libraries, universities, hospitals and schools.
What was the House of Wisdom?
The House of Wisdom was a huge academy where people studied. It was created by Caliph Harun Al-Rashid (ruled AD754 -775) and his son Al-Ma'mun (ruled AD813 - 833).
It had a big library and even an observatory where people could look at the night sky. Lots of important books were kept in the House of Wisdom.
People translated ancient Roman and Greek texts into Arabic so more people could read them.
Astronomy
Islamic astronomers improved the astrolabe which was a device that allowed travellers to find their way, a bit like a compass.

People used the astrolabe to identify the position of the sun and stars and plan their routes. Muslims could also use it to find the direction of Mecca for prayer.
Maths and science
Today, we use the Hindu Arabic number system which was founded in India. This is the ten symbols of 0, 1 ,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Mathematicians in the early Islamic world like Al-Khwarizmi introduced the system to Europe. It was much simpler to use than Roman numbers.
Al-Khwarizmi also wrote a lot about algebra which was new to the European world! Algebra is used in Maths when we do not know the exact number(s) in a calculation. In algebra we use letters to represent unknown values or values that can change.

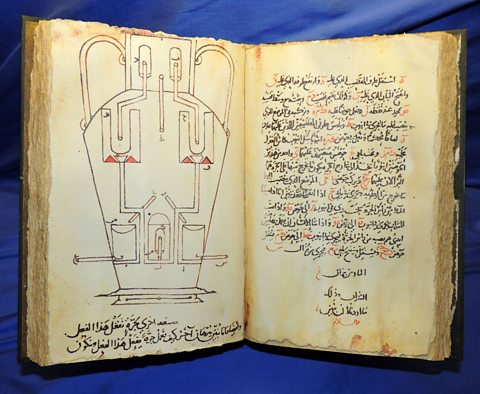
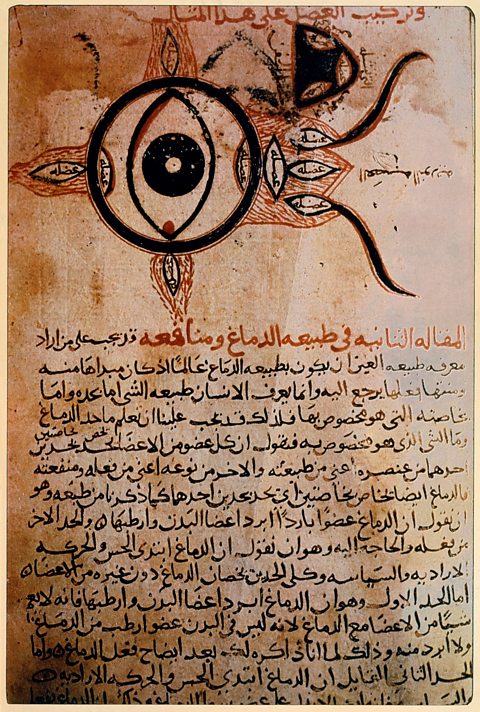
Ibn al-Haytham was a scientist who carried out experiments. He studied how the human eye worked even invented an early type of camera that helped explain how the eye sees.
Medicine
Hospitals were built in cities like Baghdad, Isfahan and Cairo in the early Islamic centuries. They were some of the first in the world and treated rich and poor people.
Records or written notes were kept about what was happening in the hospitals. They also had special hospitals for teaching.
Doctors studied the body and how to treat it for different diseases. They wanted to find out more about organs like the heart and how they worked.
Look at the table below to find out more about important figures in early Islamic medicine.
| Name | What did they study and write about? |
|---|---|
| Al-Razi | Studied diseases in children and how the brain worked. |
| Ibn Sina | Wrote an encyclopedia looking at lots of areas of medicine. It was used in universities. |
| Al-Zahrawi | Wrote a textbook about surgery and described how to use different medical tools. |
| Ibn Nafis | Studied how the heart worked and how blood moved round the body. |

Activity: Quiz – Early Islamic inventions
Bitesize Primary games. gameBitesize Primary games
Play fun and educational primary games in science, maths, English, history, geography, art, computing and modern languages.

More on Islamic civilisation
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 10
