Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Higher Tier
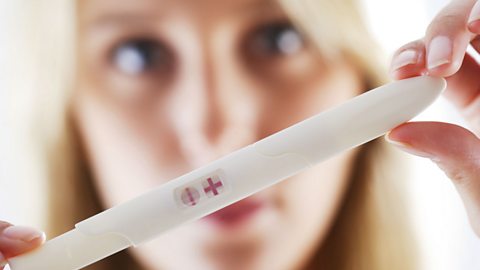
Pregnancy test kits
Pregnancy test kits use monoclonal antibodyIdentical copies of an antibody produced by fusing a spleen cell with a cancerous white blood cell which can be designed to bind to many different substances.. These have been designed to bind with a hormoneChemical messenger produced in glands and carried by the blood to specific organs in the body. called HCG which is found only in the urine of pregnant women. Monoclonal antibodies are attached to the end of a pregnancy test stick onto which a woman urinates. If she is pregnant, HCG will be present in her urine and will bind to the monoclonal antibodies on the test stick. This will cause a change in colour or pattern which will indicate pregnancy. These specific monoclonal antibodies in the pregnancy testA device which indicates if a woman is pregnant by using monoclonal antibodies which bind with the hormone HCG. will only bind with HCG.
Cancer diagnosis and treatment
cancerA disease caused by normal cells changing so that they grow and divide in an uncontrolled way. The uncontrolled growth causes a lump called a tumour to form. cells have antigenA protein on the surface of a substance (often a pathogen) that triggers an immune response.. Monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind specifically with these antigens. When injected into a person's body, the monoclonal antibodies will bind with these cancer cells and clump them together. This makes it easier to identify a tumourThe lump of cells formed as a result of uncontrolled cell division., which can then be treated or removed.
Monoclonal antibodies have also been designed to treat cancer by:
- carrying drugs that have been attached to them, to the tumour
- encouraging your immune systemThe body's defence system against entry of any foreign body, including pathogens and agents such as pollen grains. The role of the immune system is to prevent disease. to attack the cancer cells directly
Other diagnostic uses
Monoclonal antibodies are also used in a similar way to identify and diagnose infections, such as HIVHuman Immunodeficiency Virus, a disease which damages cells in the immune system. and AIDSAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome – a disease of the human immune system caused by infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)., herpes and chlamydia.
Some monoclonal antibodies have been attached to dyes that will glow fluorescentWhen a chemical absorbs ultraviolet light and releases it as visible light. under UV light. This can make disease identification much easier.