Six-mark questions
Six-mark questions are often the questions that people find the most difficult. In all longer answer questions, but especially the six-mark ones, it is important that you plan your answer and not just rush into it. After all, you would plan an essay or short story before starting. Without a plan it is easy to stray away from the key point and lose marks, get steps in a process in the wrong order or forget key bits of information.
Six-mark questions will start with command words such as ‚ÄòD±≤ı≥¶∞˘æ±≤˙±...‚Äô or ‚ÄòE≥ʱ˱Ù≤πæ±≤‘...‚Äô. The command words ‚ÄòD±≤ı≥¶∞˘æ±≤˙±...‚Äô and ‚ÄòE≥ʱ˱Ù≤πæ±≤‘...‚Äô can be confusing. If you are asked to describe a graph, you will be expected to write about its overall shape, whether it is linear or curved, the slope of gradients etc. If you are asked to explain why a pattern or trend is seen in a graph, you will be expected to use your science knowledge, not just say what you see (which is a description), eg The graph shows the number of radioactive nuclei decreases as time increases. It does this because‚Ķ.
Explain how and why questions often have the word ‘because’ in their answer. Describe questions don’t.
The number of marks per question part is given in this form [6 marks]. It is essential that you give as many different points in your answer as possible, linking these together. Often, you will be asked to compare two things - make sure that you include both in your answer otherwise you are likely to limit your score to two marks out of six marks.
Sample question 1 - Foundation/Higher
Question
Ultrasound and X-rays are waves used in hospitals to create images of the inside of the human body. To produce the image below, the waves must enter the human body.
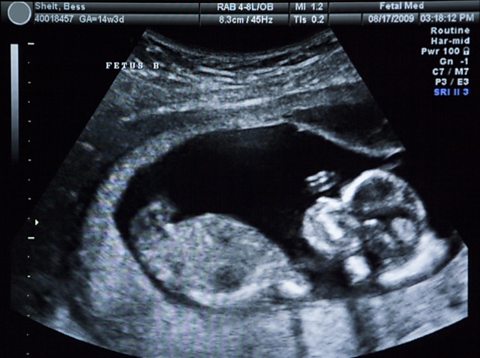
Describe the features of ultrasound and X-rays, and what happens to each type of wave after it has entered the human body. [6 marks]
This question is AQA material which is reproduced by permission of AQA.
X-rays are electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are transverse. X-rays are high energy waves that have a very high frequency and a very short wavelength. X-rays are absorbed by bone but travel through skin and soft tissues. Ultrasound is a longitudinal wave with a frequency above 20,000 Hz, which is above the range of human hearing. Ultrasound is reflected at the boundary between two different media, such as organs in the body.
You will need to describe both and include what happens to at least one of the waves inside the body. You could include the following ideas:
X-rays:
- are electromagnetic waves
- are (very) high frequency waves
- are (very) high energy waves
- have a (very) short wavelength
- are a transverse wave
- are ionising radiation
- are absorbed by bone
- travel through skin and soft tissues
Ultrasound:
- has a frequency above 20,000 (hertz)
- is above / beyond the human (upper) limit (of hearing)
- is a longitudinal wave
- is (partially) reflected at a boundary between two different media
- travels at different speeds through different media
Sample question 2 - Higher
Question
The chart shows the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum).
| Radio waves | Mircowaves | Infa-red waves | Visible Light | Ultraviolet waves | X-rays | Gamma rays |
| Radio waves |
| Mircowaves |
| Infa-red waves |
| Visible Light |
| Ultraviolet waves |
| X-rays |
| Gamma rays |
Describe in terms of their properties why they are all members of this spectrum and explain why they are arranged in the order shown. [6 marks]
This question has been written by a Bitesize consultant as a suggestion to the type of question that may appear in an exam paper.
The seven waves are grouped together because they have properties that are identical. The EM waves all travel at the same speed (3 √ó 108 m/s) in a vacuum, they are transverse, they travel in straight lines, they travel through a vacuum and transfer energy.
However, they do have different wavelengths, frequency and energy. Their order, from left to right in the diagram, is from long to short wavelength. The frequency and energy of the waves is from low to high. Gamma waves have the highest frequency and energy but the shortest wavelength. The higher the frequency or energy, the more ionising the radiation.
Answering tip: You should describe what all of the different regions have in common, and explain the difference between them and the reason they are in that order.