NARRATION:Have you ever wondered what people mean when they say, ÔÇťmy computer program has got a bugÔÇŁ? Because they definitely donÔÇÖt mean an actual bug is scurrying aroundÔÇŽ do they?
Computer programmers are human like the rest of us - they make mistakes, it happens guys! These mistakes are called bugs. Bugs stop computer programs from working how they should. And by the way, itÔÇÖs important to remember it is the computer programs that have bugs not computers themselves.
When our computer programs donÔÇÖt work as expected we need to look for the bugs. They might be simple typing errors in the program code or more serious problems in the way the instructions are organised. When we find them we can correct them and this is called debugging. ItÔÇÖs a very important part of writing a good computer program and it works best when we check for bugs as we go along rather than at the end.
LetÔÇÖs think about an everyday example, like writing a set of directions for your friend so they can meet you in the park. If just one of those directions is wrong or in the wrong order then theyÔÇÖll end up hopelessly lost. YouÔÇÖll need to make sure they are all in order and check all the turns and street names in your directions as you go, to make sure there are no mistakes or bugs. Checking and testing and then rechecking is the best way to avoid those bugs from creeping in, and to keep your friend on the right track.
ItÔÇÖs the same with computer programs. Whenever we write a new computer program, the chances are there will be bugs. ItÔÇÖs important to check and debug right from the start. We notice bugs when something doesnÔÇÖt work the way we want it. So if we test our program as we go along we can spot any mistakes before they get too big.
Take computer games for example. I like to download new features and characters as soon as they come out. The trouble is, the first version of the updated program usually has loads of bugs that havenÔÇÖt been tested properly. This can lead to all sorts of problems like game controllers going wrong, graphic glitches and characters behaving strangely. ItÔÇÖs always better to wait for the program update to be debugged before rushing to download.
An example of a bug causing problems on a much bigger scale was the Mariner 1 spacecraft back in 1962. The spacecraft was programmed to visit the planet Venus nearly 200 million miles away and send back information to scientists here on Earth. Unfortunately, someone had typed the wrong symbol into the program code somewhere and hadn't spotted the mistake. Mariner 1 had to be destroyed just 290 seconds after launch to prevent it crashing back to Earth. This turned out to be an eighteen million dollar bug! Ouch, that's a nasty bite!
One of the keys to debugging is knowing what your program is meant to do. This means going back to the original algorithm, or list of instructions, and comparing this to what is actually happening when the program runs. Then you can debug, and test, and debug, and test again. Another thing to remember is that problem solving is always easier with friends to help. ItÔÇÖs the same with debugging. Programmers will often work together in teams to debug big and complicated projects.
So what are you waiting for? Get together and get exterminating - Dr Who style!
Video summary
This short film uses computer games to explain debugging, which is the process of finding and correcting errors in computer programs.
Giving directions to get the park is also used as an example to explore the strategies needed for debugging, including checking and rechecking as you go.
This short film also looks at how bugs are often found in updated programs like computer games. The destruction of the Mariner 1 space probe is given as an example of how a small but undiscovered bug led to a huge problem.
Finally, some basic strategies for debugging are explored, including working with a team, and referring back to the original program algorithm to check the intended outcomes.
This short film is from the 91╚╚▒Č Teach series, Cracking Computing.
Teacher Notes
A good place to start is with errors in a simple sequence of instructions given to a robot, either on screen or in real life. Once the outcome has been agreed the program can be run and any mistakes identified. The error can be rectified, the program rerun and the outcome checked again. This will model the check, test, check again process that is important for successful debugging.
Unplugged activities where pupils work in pairs to give instructions to each other for drawing an unseen character are also great for identifying where the actual outcome differs from the intended outcome, and how this happened.
Many activities and games used to watch coding have built in lessons that focus on debugging by deliberately introducing mistakes that pupils have to find and correct. Working through some of these activities as a whole class can be useful to model strategies.
Pupils should wherever possible write and debug their programs in pairs of groups, to develop their collaboration skills.
Other subjects
English: Pupils are familiar with checking their work for spelling and grammar errors and then editing and adapting their work to correct these mistakes. These experiences can be compared with checking a computer program for errors and debugging it.
PE: Pupils are often asked to learn a physical process like completing a forward roll, or dribbling a ball around cones, where there is a clear expected outcome. Photography and video can be used to capture the process and identify errors in the process. These errors can then be addressed and hopefully the outcome improved - this could be seen as a type of debugging.
This short film is suitable for teaching:
- KS2 computing curriculum in England
- Technologies curriculum area at 2nd Level in Scotland
- KS2 digital competence framework in Wales
- KS2 using ICT cross-curricular skill in Northern Ireland
Algorithms. video
This short film for primary schools outlines how algorithms are sets of instructions to make something happen, before explaining further using a recipe analogy.

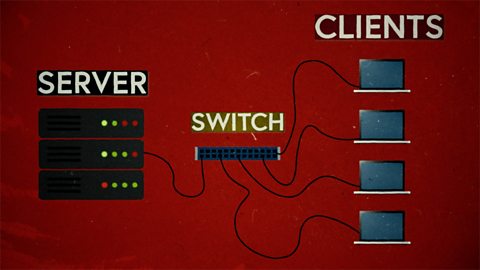
Computer networks. video
This short film explains computer networks. It looks at different types of computer network and the elements that make up a basic network including clients, servers, switches and hubs.
Creating with computing. video
This short film explores the many creative computing tools we have access to, with a focus on how they are used to create new creative content and media.

Decomposition. video
This short film explains how decomposition involves breaking one big problem down into smaller, more manageable problems that can be tackled step by step.

Input and output. video
This short film gives a brief history of input and output methods with examples, and brings us up to date with examples of familiar input and output devices that we use every day.

Logical reasoning. video
This short film outlines logical reasoning as ÔÇśsensible thinkingÔÇÖ when following rules, and explains how a problem with a computer program can be solved using logical reasoning.

Repetition. video
This short film for primary schools explains how repetition within computing allows a command to be repeated to make a computer program more efficient.

Search technologies. video
This short film gives a brief history of the development of the internet and the invention of the world wide web by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, and explains the role of a search engine.

Selection. video
This short film covers the use of selection in simple computer programs, and shows how this idea of yes/no questions can allow computers to respond to external conditions and select different paths.

Sequencing. video
This short film covers the concept of sequencing, or making sure things are in the right order, and explores what might happen if things are done in the wrong order, or sequence.

Variables. video
This short film explores how computers use variables to store things that change, like names, numbers and scores.

Working with data. video
This short film explores how data is collected using digital devices in response to questions, and how it is organised into tables, records and fields on a computer system.
