Part-whole model
Here is a part-whole model.
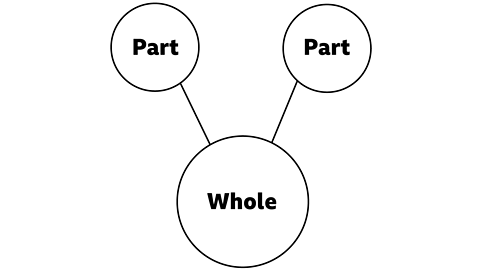

Sometimes the model is rotated. It looks different, but it still has two parts and a whole.
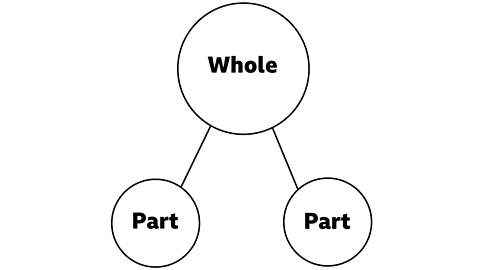
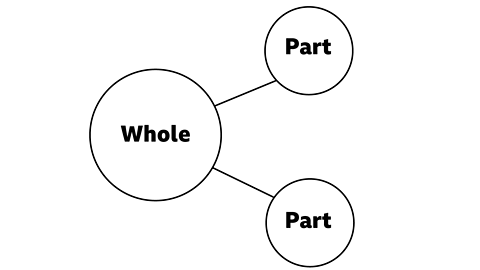
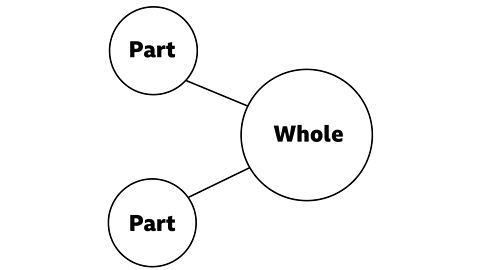
We can use this model to help us solve problems.
Addition
What is 4 + 5?
We can put 4 things in one of the parts and 5 in the other part.
By combining the two parts in the whole circle we can find the sum of 4 + 5.
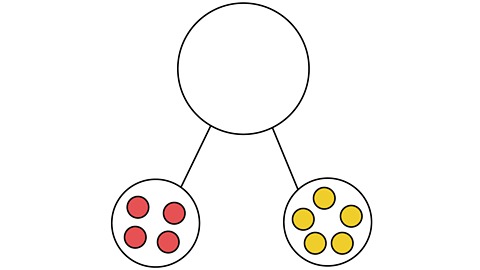

The answer will look like this.
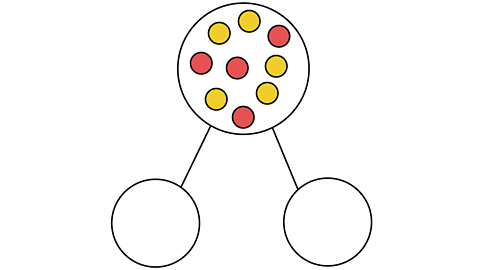

We can also use numbers instead of counters.
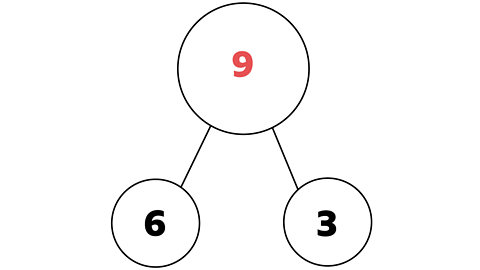
This model shows 6 + 3 = 9.

You can also use part-whole models to help with addition problems involving bigger numbers.
Example 1
What is 25 + 14?
We can partition the smaller number and add the tens and ones separately.
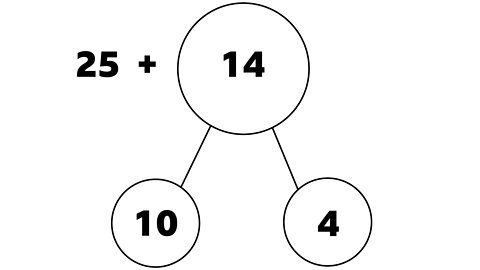
We can use the part-whole model to split 14 into 1 ten and 4 ones.
It's much easier to add 10 to 25, then add the 4.
25 + 10 = 35
Then add the 4.
35 + 4 = 39

Subtraction
Let’s take a look at subtraction now.
Subtraction is where we know the whole and only one of the parts.
So this question 12 – 5 = ? would look like this as a part-whole model.
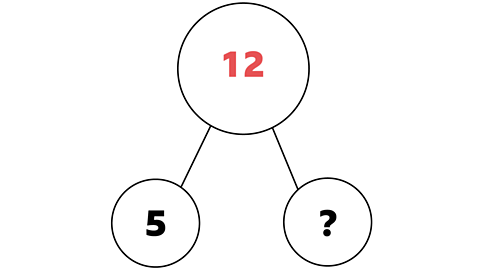

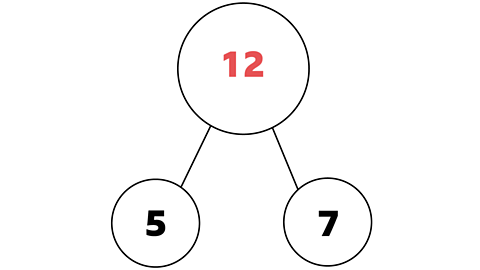
It is telling us we need to subtract the part from the whole to find our answer (which is the missing part).
12 - 5 = 7
Just like with addition, we can use a part-whole model to help partition larger numbers to make them easier to deal with in subtraction problems.
Example 2
What is 35 – 14?
First, partition 35 into 30 and 5.
Then we can look at the number 14 and subtract 10 from 30 and subtract 4 from 5.
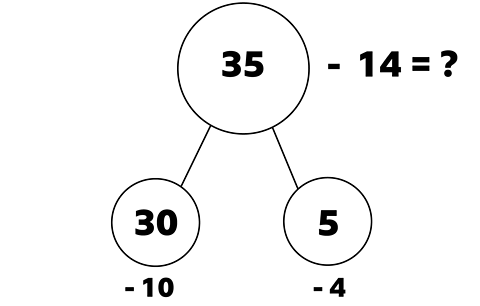

First subtract the tens from each number.
30 – 10 = 20
Then subtract the ones in each number.
5 – 4 = 1
We then recombine the two numbers to make the answer 21.
25 – 14 = 21
Some subtraction questions are more challenging and need us to partition the whole more flexibly.

Example 3
What is 43 - 18?
Look at how this number was split.
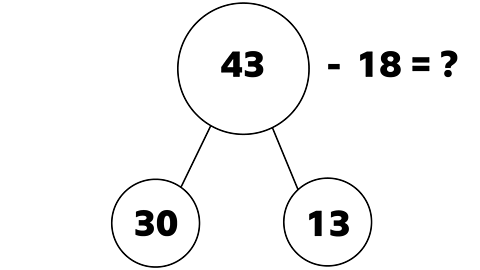

- What do you notice?
The split isn’t tens and ones. This time it has been split into 30 and 13.
If you add 30 and 13 together it makes 43.
- Why split 43 in this way?
The 8 ones in 18 is bigger than the ones digit in 43, so it would make subtracting one from the other difficult.
If the number 43 is split into 30 and 13, it is possible to subtract 8 from 13.
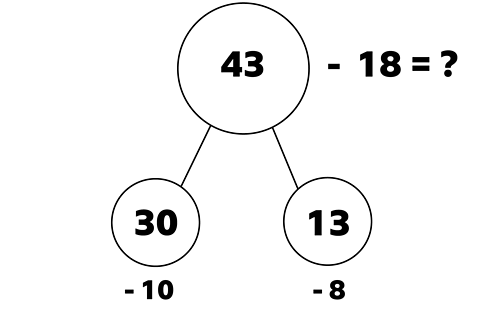
13 – 8 = 5
And then:
30 – 10 = 20
By recombining 20 and 5 into 25 we are now able to solve this problem.
42 – 18 = 25

Activity
Karate Cats Maths game. game
Train with the Karate Cats to become an expert in addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, place value and more!

More on Adding and subtracting
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 14

- count11 of 14
- count12 of 14

- count13 of 14
