Geometric skills
Determine the gradient of a straight line
The gradient of a straight line is how steep it is. It can be calculated from a given set of coordinate points. There are three special cases of straight lines: parallel, horizontal and vertical.
Circle geometry
Arc length is a fraction of circumference. Area of a sector is a fractions of the area of a circle. Both can be calculated using the angle at the centre and the diameter or radius.

Calculating the volume of a standard solid
The volumes of standard 3D solids can be found using specific formulae. In this SQA National 5 Maths revision guide, we'll go through how to work out the volume of a cylinder, sphere, hemisphere, cone, prism, and composite shapes.
Applying Pythagoras Theorem
Pythagoras Theorem states that for a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.

Applying the properties of shapes to determine an angle
Angles in a triangle add up to 180掳 and quadrilaterals add up to 360掳. Angles can be calculated inside semicircles and circles, as well as with perpendicular bisectors and tangents.

Using similarity
Similar figures are identical in shape, but not necessarily in size. A missing length, area or volume on a reduction/enlargement figure can be calculated by first finding the scale factor.
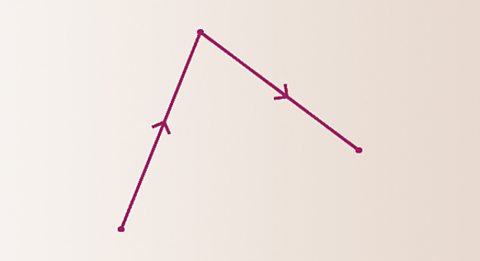
Working with two-dimensional vectors
A vector describes a movement from one point to another. 2D vectors are added from nose to tail giving a new line from the starting point to the final point..
Working with three-dimensional coordinates
A vector describes a movement from one point to another. 3D vectors exist in the xyz plane. The 3D coordinates for any point have three values.
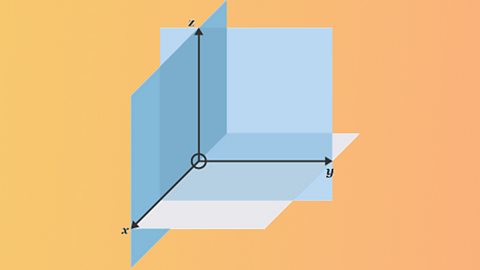
Using vector components
Vector components describe the separate x, y and z values of a vector. When working with vectors, components can be added or subtracted separately.
Calculating the magnitude of a vector
The magnitude of a vector is its size. It can be calculated from the square root of the total of the squares of of the individual vector components.

Video playlist
An Approximate History of Co-ordinates. Video
An animated look at the work of Rene Descartes and the cartesian co-ordinate system.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link