Nutrition, digestion and excretion
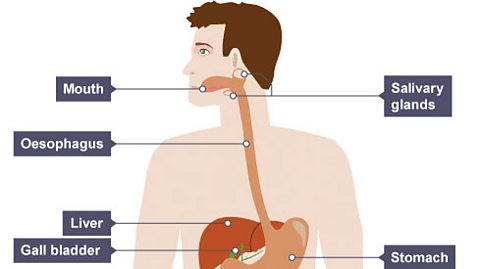
Structure of the digestive system
The digestive system is made up of key parts, each of which has a different function.
Digestive enzymes and absorption
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions including digestion.

Food energy
Food is a store of energy, transferred from the food to the consumer.

Healthy diet
A balanced diet contains the correct amount of all food groups.

Malnutrition
There are two types of malnutrition: when and how do they occur?

Obesity
'Obese' is a medical term used to describe a person with a high excess of body fat.

Lipids, oils and fats
Lipids include fats (solid at room temperature) and oils (liquid at room temperature).

Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins and minerals help the body to use other nutrients efficiently.

Protein
Proteins are a vital part of a healthy diet. Protein-rich foods include fish, meat, eggs and beans.

Dietary fibre
Dietary fibre is plant material that cannot be digested by the human body.

Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy in a healthy diet. Starchy and sugary foods are high in carbohydrates.

Starch
Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.

What is poo?
Poo (faeces) is the waste that remains after food has been digested and its nutrients absorbed by the body.
Modelling the digestive system
Try this experiment and recreate processes in the digestive system with online and lab options.
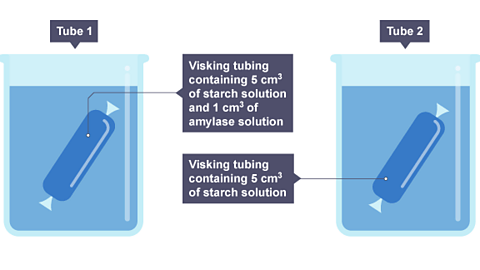
How to model digestion using tights
Learn how digestion works and how to model digestion using a pair of tights.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription