Exam practice
GCSE Chemistry: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Chemistry past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Chemistry: exam-style questions
CCEA Foundation and higher GCSE interactive tests based on past papers to get you ready for your chemistry exams. Topics include the periodic table, equations and more.

GCSE Chemistry: quick-fire questions
Use our interactive quiz to understand how the CCEA foundation and higher chemistry GCSE exams work. Revise topics such as the periodic table and equations.

Quizzes
QUIZ: Acids, alkalis and salts (1)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying acids, alkalis and salts. Test your knowledge on neutralisation, reactions with acids and solutions.

QUIZ: Acids, alkalis and salts (2)
This interactive quiz is for GCSE Chemistry (single science) students studying acids, alkalis and salts. Test your knowledge of indicators, reactions and chemical equations.

Structures, trends, chemical reactions, quantitative chemistry and analysis
Atomic structure - (CCEA)
Scientists’ ideas about atoms have changed over time. Today, they agree that atoms have a positively-charged nucleus made of protons and neutrons, and negatively-charged electrons that orbit the nucleus in shells.

Bonding - (CCEA)
Atoms and ions bond with each other in three main ways – ionic bonds, covalent bonds and metallic bonds. Different types of bonds form different types of structures – lattices and molecules.
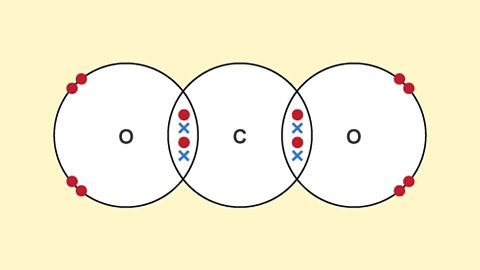
Structures - (CCEA)
Ionic bonding holds ions together in a giant lattice. Covalent bonds create simple molecules or giant covalent structures. Different types of bonding give a substance different properties.

Nanoparticles - (CCEA)
Nanoparticles have large surface to volume ratios. This gives them interesting properties.

Symbols, formulae and equations - (CCEA)
Symbols, formulae and equations help chemists to explain chemical reactions in detail.

The periodic table - (CCEA)
The periodic table helps to categorise the known elements and make predictions about ones that we haven’t yet discovered.

Quantitative chemistry - (CCEA)
Chemists use relative atomic masses and relative formula masses to carry out mole calculations.

Acids, bases and salts - (CCEA)
Many chemicals are acidic, neutral or alkaline. We can distinguish one from another using indicators. Acidity and alkalinity are measured on the pH scale. A salt is formed when an acid is neutralised by an alkali.

Chemical analysis - (CCEA)
Most elements are rarely found in their pure form. They are found chemically combined with other elements in compounds. Compounds are often found mixed with other compounds. Mixtures may be separated and analysed.

Solubility - (CCEA)
Solubility is a measurement of the maximum mass of a substance which will dissolve in 100 g of water at a particular temperature. The solubility of solids and gases in water varies with changes in temperature.

Further chemical reactions, rates and equilibrium, calculations and organic chemistry
Metals and reactivity series - (CCEA)
The reactivity series ranks metals by how readily they react. More reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their compounds and react with water.

Redox, rusting and iron - (CCEA)
Oxidation is loss of electrons, gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen. Reduction is gain of electrons, loss of oxygen or gain or hydrogen. Rusting is an example of oxidation.

Rates of reaction - (CCEA)
The rate of reaction increases when reactant particles successfully collide more frequently. Temperature, reactant concentration, size of solid reactant particles (surface area) and catalysts can all affect the reaction rate.

Reversible reactions - (CCEA)
Some chemical reactions are reversible, and may reverse even as they react. This can create a state of dynamic equilibrium.

Organic chemistry - (CCEA)
An organic chemical contains the element carbon. There are four different homologous series of organic compounds discussed here: alkanes, alkenes, alcohols and carboxylic acids.

Quantitative chemistry - (CCEA)
We looked at calculating and using moles for solids using mass in unit 1.7. Here we are using moles of a solute dissolved in a solution and moles of a gas to carry out calculations.

Electrochemistry - (CCEA)
Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down electrolytes. The products of electrolysis can be predicted for a given electrolyte.

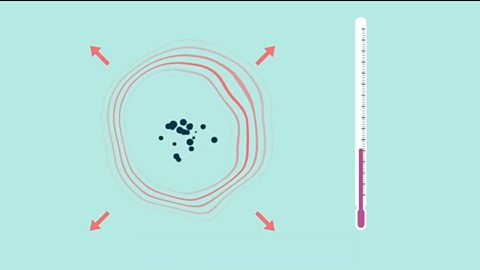
Energy changes in chemistry - (CCEA)
When a chemical reaction occurs, energy is transferred to, or from, the surroundings. An exothermic reaction releases heat to the surroundings and an endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
Gas chemistry - (CCEA)
The Earth atmosphere is a mixture of gaseous elements and compounds. We can prepare samples of common gases such as hydrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide in the laboratory and examine their properties and reactions.

Prescribed practicals
1. Determine the mass of water in hydrated crystals
In this experiment you will heat hydrated iron(II) sulfate crystals. By carefully heating the crystals and recording mass measurements, we can calculate the mass of water in the supplied crystals.
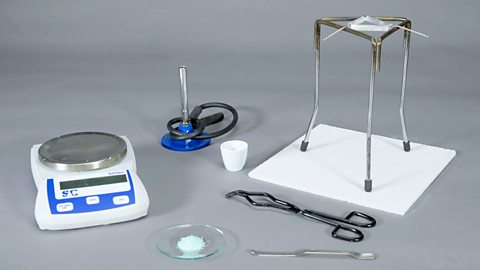
2. Investigate the reactions of acids
Investigating the reactions of acids, including temperature changes that occur.

3. Investigate the preparation of soluble salts
Making a soluble salt from a base and making a soluble salt from an alkali.

4. Identify the ions in an ionic compound
Identifying the ions in an ionic compound using chemical tests.

5. Investigate the reactivity of metals
Determining the relative reactivity of metals.

6. Investigate the rate of reaction
Looking at how quickly magnesium reacts with dilute hyrdrochloric acid.

7. Investigate the reactions of carboxylic acids
A carboxylic acid is one which contains -COOH as its functional group. In comparison to mineral acids, carboxylic acids show some similarities, but also, some important differences.

8. Titration
Determine the reacting volumes of solutions of acid and alkali by titration and determine the concentration of solutions of acid and alkali by titration.

9. Investigate the reaction of gases
Investigate the preparation, properties, tests and reactions of the gases hydrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide.

Practical skills
Practical skills - (CCEA)
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link